How to Easily Integrate an API Key Into Your Website!
Table of Contents
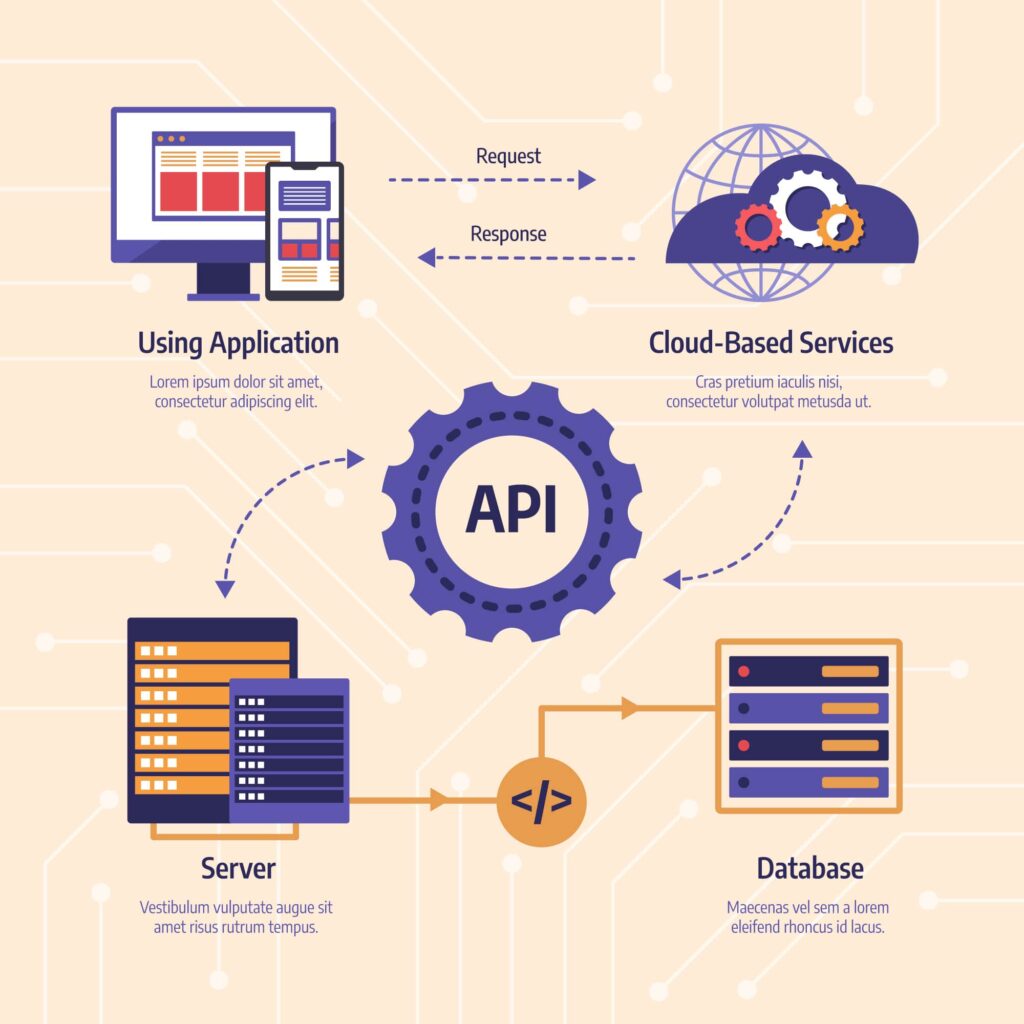
When you generate an API key, you’re essentially getting a unique code that allows software to communicate and share data securely between different systems.
This key plays a vital role in authenticating and authorizing access to resources and features that are offered by a service provider. As a developer or business, you need to manage and control this key carefully to ensure that only the right users have access to the data or services. With the right permissions set for your API key, you can prevent unauthorized users from making too many requests, which could disrupt the normal function of your website.
By creating variables to store the API key securely within your backend or frontend environment, you ensure that security is maintained. For example, JavaScript can be used to fetch and display requested data from the endpoints of third-party organizations, making it an easy way to update the content of your site.
This method helps you seamlessly integrate API keys into your applications while ensuring that you stay within the limits and methods provided by the API service.
how to use api key in website (Quick Answer)
- To use an API key on your website, follow these steps:
- Generate an API key from the service provider.
- Store the API key securely in your backend or frontend code.
- In your code, use the key to make API calls by including it in the request headers or URL.
- Ensure you handle the response data properly to display it on your website.
What is an API key?
An API key is essentially a key or ID that allows you to access certain applications and their features securely. It’s used to prevent unauthorized access to potentially sensitive info that these applications may want to share with others. The API key is usually a string of letters and numbers that’s transmitted with every API call, which helps the system identify the requests being made.
However, unlike a real ID, an API key does not directly identify the users themselves but ensures that only authorized users can interact with the system.
What are API keys used for?
API keys serve multiple important functions in website development. They ensure security by verifying that only authorized users can make requests to access sensitive data and resources. These keys also help with monitoring and limiting usage, providing authorization to the API and ensuring that usage stays within set boundaries. By managing access control, developers can protect their system from overuse or abuse, which is crucial for maintaining smooth service. Below are some key uses of API keys:
Security layer to lock down data between API and client
Access control to ensure that only authorized users can access specific resources
Tracking and billing to monitor API usage and manage billing purposes
Rate limits enforcement to prevent misuse of the API by restricting excessive requests
Integration of services or software, allowing them to communicate efficiently and securely
Helps in software development by keeping systems secure, efficient, and responsible
Advantages of using API Keys
API keys provide a powerful solution for controlling, monitoring, and securing access to applications, data, and resources.
They act as enablers for creating more innovative services by ensuring security and enabling access control. By using API keys, developers and businesses can manage who gets access to sensitive data and easily track usage.
This helps prevent unauthorized access and can even allow users to revoke access when necessary, ensuring sensitive information stays protected.
Additionally, API keys offer several performance benefits. For instance, they can help in optimizing the performance of applications by enabling caching, which reduces the need for frequent requests.
This leads to a boost in performance, making applications more responsive, scalable, and efficient. Rate limiting is another advantage, ensuring that API calls are made in a controlled manner, avoiding issues like denial-of-service attacks.
Load balancing also ensures that API requests are distributed efficiently across servers, maintaining scalability and preventing bottlenecks.
Customization allows developers to assign unique access to each user or application, providing more flexibility in how they integrate different services or test performance without affecting existing applications.
What are the types of API keys?
When using API keys, the type you choose depends on the use case and security requirements of your application. Selecting the right API key is important to ensure you protect sensitive data and avoid unauthorized access. Different types of API keys are suited for various scenarios, such as securing public data, limiting access to specific resources, or providing temporary access.
Public API keys: Used for read-only access to public data, often embedded in client-side applications.
Secret API keys: For accessing sensitive data and write access, typically found in server-side applications.
JWT-based API keys: Utilize JSON Web Tokens for authentication and authorization, common in modern web applications.
Session-based API keys: Provide temporary access for a short session, expiring after a set time.
Scoped API keys: Limit access to certain features or resources, providing control access.
How to generate an API key
To generate an API key, start by logging into the relevant API platform or service. Navigate to the section or setting where you can create the key. After selecting the type of key you need, provide a name or a descriptor for it, and then proceed by copying the key. It’s important to store the key securely, either in a password manager or an encrypted file, just as you would with physical keys. Make sure not to share the key publicly and ideally keep it in a safe location. Also, remember to rotate the key periodically to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
Create a Variable to Store the API Key
When you generate your API key from the API platform, the first step is to store it securely. After copying the key from the service’s appropriate section or setting, create a variable in your code to keep the key. For better security, store this variable in a password manager or an encrypted file. It’s important to avoid sharing the key publicly and always keep it in a safe location.
For example, in JavaScript, you can store the key in a variable like this:
const apiKey = 'your-api-key-here';To minimize the risk of unauthorized access, remember to rotate your API key periodically. This simple practice ensures that your application remains secure.
Create Variables for the API Call
When making an API call, you’ll often need to use query parameters to customize the request. Your application must be able to accept user input and store it in variables. For example, if you’re using the OpenWeather API to get Current Weather Data, you’ll need to collect the city name from the user. You can also specify additional details, like the state code and country code, especially since there are many cities with the same name across different locations. Based on the documentation, this input can be stored in a variable, like city, to help your application make the correct API call.
Here’s an example in JavaScript to store the city name:
let city = "New York";
Note: Searching by state codes is only available for locations in the United States.
Construct a Query URL to Make the API Call
To make an API call, you first need to construct a query URL using the API key and user input. For example, with the OpenWeather API, you’ll create a URL for Current Weather Data by including the city name, like this:
api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q={city name}&appid={API key}.
You can replace the placeholders with the variables you created, such as the city variable and API key variable. According to the documentation, the required parameters are q (the city variable) and appid (the API key variable). Other optional parameters are also available, but for this example, you’ll focus on these two. The parameters section of the documentation will provide further details on how to customize your request.
Make the API Call Using Fetch
To make an API call using the Fetch API, you’ll need to pass the query URL as a parameter. The Fetch API is built directly into the browser, so you don’t need to use tools like AJAX or a bulky library like jQuery. Once you have the query URL, you can simply use
fetch(queryURL)
to send the request. However, make sure your application is set up to accept user input, and store that input in the city variable you created earlier. This will allow the URL to function properly when making the request.
Handle the Response Data
After your API call is made and you receive the response data, you can use it within your application. The query you sent will return the API data, and it will work similarly to an API that doesn’t require an API key. At this stage, you’ll handle the returned data and incorporate it into your app. As you progress, you’ll learn how to better protect your API keys and manage API calls on the back end, but for now, this approach will get you started with handling response data easily.
What Do I Do with an API Key?
Once you have an API key, you use it to access services and data from an API. It provides project authorization and links usage information to your project. The Extensible Service Proxy (ESP) ensures only authorized projects can make requests, rejecting any calls from projects that haven’t been granted access or enabled for the API.
How to use API in our website?
Find an API that meets your needs.
Read the documentation to understand the terms.
Make an API request and test the API.
Request an API key for authentication if needed.
Interpret the response to ensure it fits your requirements.
How to activate an API key?
Go to the Google Cloud console for your project.
Navigate to APIs & services.
Open the Library page.
Click on Private APIs.
Find and click the API you want to use.
In the information page, click Enable to activate the API.
Conclusion
In conclusion, integrating an API key into your website is a powerful way to enhance functionality and access external services securely. By following the steps outlined above, you can easily set up API keys, handle requests, and manage the data that powers your website. Remember to always store your API keys securely, manage your permissions carefully, and follow best practices to ensure smooth and secure operations.
Additionally, while managing your website’s backend, it’s crucial to Back Up Your WordPress Website via cPanel regularly to avoid data loss and ensure that your site remains secure and up-to-date. A well-maintained website, with securely integrated APIs and consistent backups, is key to delivering a seamless experience to your users.
Take the necessary steps today to safeguard your data and elevate your website’s functionality!
More Informational Articles

Maryam Ahmed
Hi! I’m Maryam Ahmed, a passionate Web Designer and Developer with over 2 years of experience. I specialise in creating custom websites – from simple and elegant designs to fully dynamic and animated sites
ABOUT ME !!

Maryam Ahmed
With a passion for modern design and functionality, I create custom websites that are visually appealing, dynamic, and SEO-friendly. From personal blogs to business platforms, I bring your vision to life with creative design and expert development.
RECENT POSTS

Top Web Design Services for Modern Businesses

10 Web Design Tips to Make Your Website Stand Out in 2025

Website Development Basics: A Simple Guide for Beginners

Why Your Social Media Marketing Strategy Isn’t Working

Master UI UX Design with Google and the Best Free Courses Online.

Best WordPress Themes for Modern Business Websites